The Code and Code Compliance
What is World Anti-Doping Code
The World Anti-Doping Code (Code) aims to harmonise anti-doping policies, rules and regulations within sports organisations and public organisations. The Code works in conjunction with eight International Standards. WADA oversees the acceptance, implementation and compliance of the Code.
ADO Guide to the Code
Athlete Support Personnel Guide outlines the changes in the 2021 Code and highlights what Anti-Doping Organisations (ADOs) should focus on going forward from a practical standpoint. It should be noted that the Guide is neither a substitute for the language of the Code, nor for the anti-doping rules of an ADO. The language of the Code is always the primary source.
What is ‘Code Compliance’
Code Signatories – National Anti-Doping Organisations (NADO), International Federations (IF) and Major Events Organisations (MEO) – are responsible for the implementation of the Code through policies, statues, rules, regulations and programmes according to their authority and jurisdiction.
All Signatories have to abide by a number of Code Compliance obligations.
How to Become Code Compliant
Steps for a NADO to become Code Compliant:
Step 1: Acceptance
- Agree to both the principles of the Code and implement and comply with the Code.
- Develop the NADO Rules based on WADA’s Model Rules for NADOs. The Rules need to be submitted to WADA for review and acceptance.
Step 2: Implementation
- Develop or amend existing local NADO policies, statutes, regulations, etc. to include the mandatory articles and principles of the Code.
- Translate the revised NADO rules and revised NADO policies etc. into your respective official language (if necessary).
Step 3: Code Enforcement
- Inform National Federations (NF) of the revised NADO rules and policies in accordance with the Code.
- Ensure NFs sign an undertaking to abide by the Code and the relevant anti-doping policies.
Is it Mandatory to be Code Compliant?
It is mandatory for Signatories (NADOs, IFs, and MEOs) of the Code to ensure compliance of the Code.
The Code states “The Signatories shall implement applicable Code provisions through policies, statuses, rules or regulations according to their authority and within their relevant spheres of responsibilities.”
Compliance Monitoring Programme
WADA’s Compliance Monitoring Programme represents a thorough review of anti-doping rules and programmes, and aims to reinforce athlete and public confidence in the standards of ADOs work worldwide. The program is guided by its Compliance Strategy.
Programme Components
Code Compliance Questionnaire (CCQ): The CCQ is a tool to measure compliance of Signatories with the mandatory requirements of the Code and International Standards.
Audits: Due to limitations of a self-assessment questionnaire, in-person and desk audits of Signatories are conducted by trained individuals from WADA and external experts in anti-doping.
Continuous Monitoring Program: The Continuous Monitoring Program complements the aforementioned tools by bridging the gap between CCQs and the follow up of audits.
Other Sources: Other sources of information are also used to monitor and assess the quality of anti-doping programmes and their subsequent compliance with the Code and International Standards. This include ADAMS, the Agency’s results management database; investigations; and any other intelligence received to monitor Signatories’ compliance with the Code.
Ongoing WADA Support: WADA continually provides Signatories with assistance and guidance in implementing and complying with the Code and International Standards, particularly as the Compliance Monitoring Programme identifies areas for improvement.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
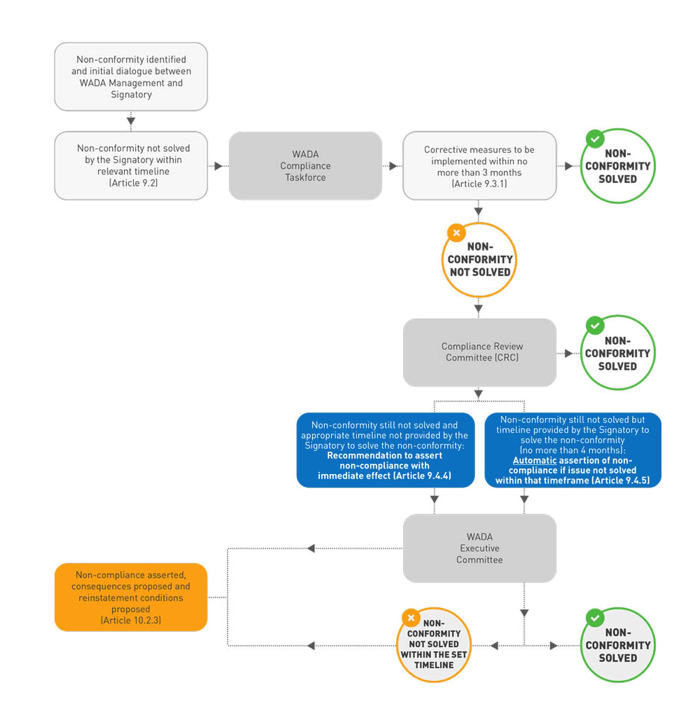
A legal framework for consequences of non-compliance was set by the International Standard for Code Compliance by Signatories (ISCCS). If any non-conformity is identified, the Taskforce facilitates an open dialogue with the Signatory concerned and recommends corrective actions. Support and assistance are provided to help Signatories address all non-conformities within an agreed timeframe.
The range of consequences that may be imposed on a Signatory that has failed to comply with the Code and/or International Standards on Annex B of the ISCCS.
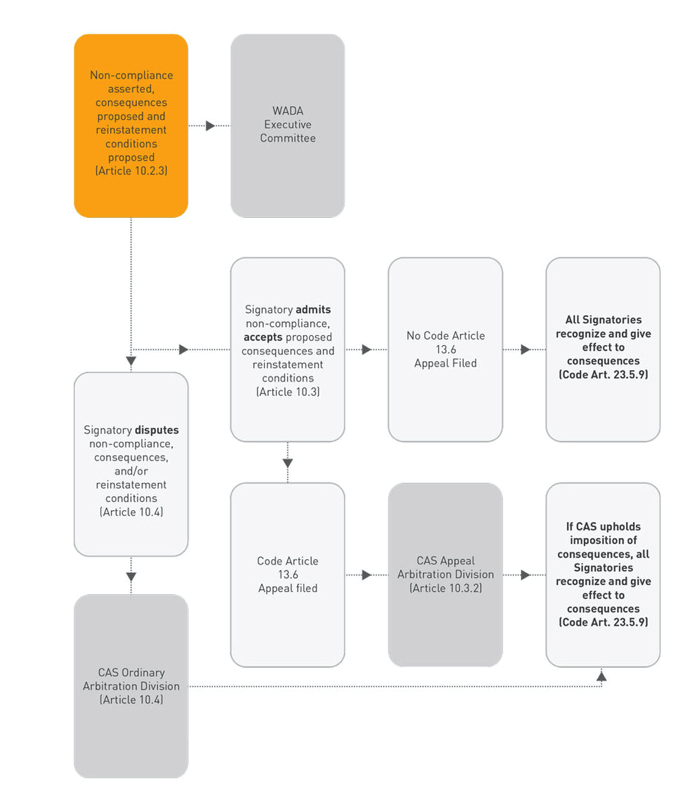
Procedure to be Followed when Non-confirmities are Identified
Procedure to be Followed AFTER Non-Conformities is Asserted